
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have rapidly transformed various industries, including healthcare. From disease diagnosis and prediction to drug discovery
Erythropoietin (EPO) 4K to 10K I.U is a synthetic form of a natural hormone that stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow. It is commonly used to treat anemia caused by chronic kidney disease, chemotherapy, or certain medical conditions where red blood cell levels are low. EPO works by signaling the body to increase red cell output, improving oxygen delivery to muscles and tissues. This helps boost energy levels, reduce fatigue, and enhance overall physical performance. It is administered under medical supervision and plays a key role in restoring and maintaining healthy blood counts.
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone responsible for stimulating red blood cell production in the bone marrow. In patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially those on hemodialysis, the kidneys fail to produce enough EPO, leading to anemia. To correct this, recombinant forms like Epoetin alfa, Darbepoetin alfa, or CERA are commonly used.
Anemia is a frequent complication in dialysis patients due to impaired erythropoietin production, iron deficiency, and frequent blood loss during treatment. Supplementing with EPO helps:
Restore and maintain hemoglobin (Hb) levels
Improve oxygen delivery to tissues
Reduce the need for blood transfusions
Enhance patient energy and quality of life
This dose range is considered standard for maintenance therapy in hemodialysis patients. It is adjusted based on patient-specific factors and hemoglobin response. EPO can be administered 1 to 3 times per week, either intravenously (IV) post-dialysis or subcutaneously (SC) in select cases.
| Dose Range | Frequency | Route | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4,000–6,000 IU | 1–3 times/week | IV or SC | For stable Hb around 10–11.5 g/dL |
| 7,000–10,000 IU | 1–2 times/week | IV or SC | For patients with low Hb or EPO resistance |
Ideal Hb levels are 10–11.5 g/dL
Levels above 12 g/dL are avoided due to risk of thrombosis, hypertension, and cardiovascular events
Adjustments to dosing are based on regular Hb monitoring
Higher doses (up to or above 10,000 IU) may be required in cases of:
EPO resistance from inflammation or infection
Iron deficiency, despite supplementation
Blood loss, recent surgery, or inadequate dialysis
Secondary hyperparathyroidism, affecting erythropoiesis
Iron parameters – Ferritin > 200 ng/mL, TSAT > 20%
Signs of inflammation or infection
Dialysis adequacy – Kt/V ≥ 1.2
PTH levels – To rule out bone marrow suppression
Erythropoietin 4,000–10,000 IU is a critical therapy for managing anemia in hemodialysis patients. The dose is tailored to each patient’s hemoglobin levels, response, and clinical condition. Effective use requires close monitoring, proper iron supplementation, and adjustment based on treatment goals and guideline recommendations.



















Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have rapidly transformed various industries, including healthcare. From disease diagnosis and prediction to drug discovery
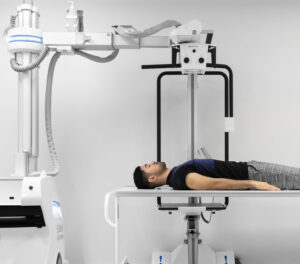
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, advancements in technology continue to reshape the way we diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Ut wisi enim ad minim veniam, quis laore nostrud exerci tation ulm hedi corper turet ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer

To build a future in which hospitals don’t have to fight to find dependable, high-quality, and affordable medical supplies.

TOWER-6, Blossom County, Paras
Tierea, Sector 137, Noida, Uttar
Pradesh 201305
Copyright © 2024 Ren HealtQare all rights reserved.
WhatsApp us